Musculoskeletal and osteomuscular system – a single complex, consisting of bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, nerve structures, which provides support and spatial movement of the human body, and movement of individual body parts and organs.
The symptomatic therapy means of musculoskeletal system pathology are non-steroidal and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These drugs relieve pain, eliminate inflammation in the joints, but do not affect the recovery of the affected cartilage tissue. Therefore, the method of choice is the method of administration of stem cell injections for arthritis osteoarthrosis since use of stem cell therapy can eliminate the cause of the disease, and also its consequences.
All diseases of musculoskeletal system can be divided into two large patient groups which can equally regard information about stem cell therapy.
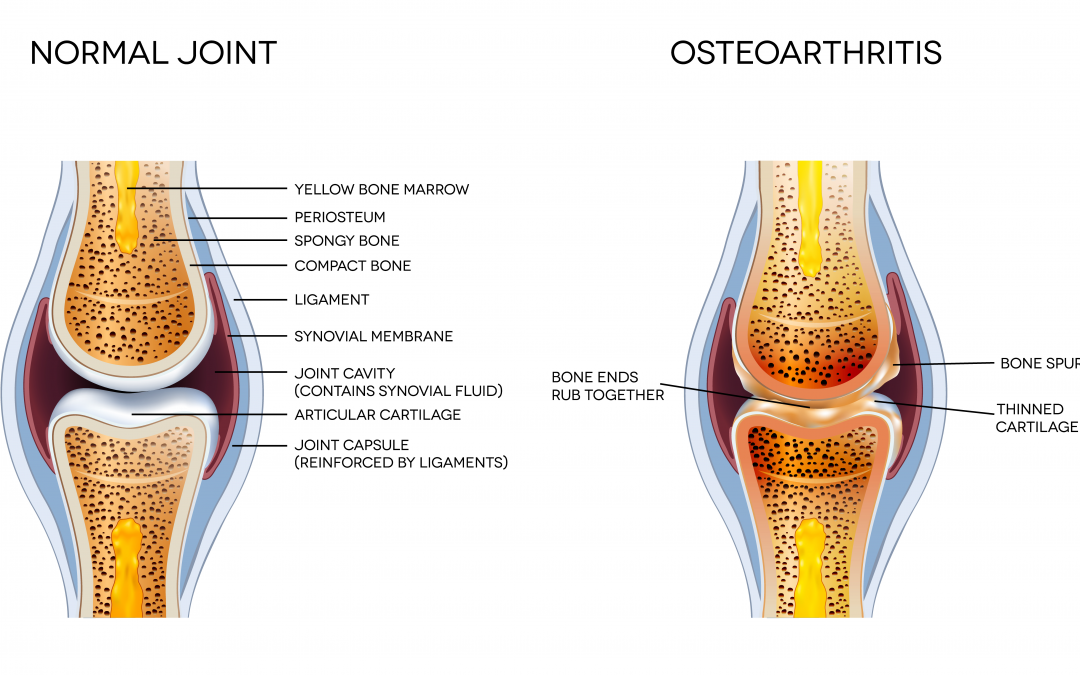
The first group consists of the diseases, the development of which may result in degenerative changes of the articular surfaces, cartilage and surrounding tissues. Under osteoarthrosis the cartilage degeneration occurs until the complete destruction, followed by sclerosis of mating surfaces of the bones with the growth of osteophytes, which ultimately leads to the development of strains, sprains and joint dysfunction in case of absence of doctor intervention with therapy by mesenchymal stem cells. Osteoarthritis – the most common joint disease, comprising almost 70-80% of all the joint pathology reacts to the treatment by stem cells therapy for osteochondrosis.
The second group of musculoskeletal system diseases includes arthritis. Stem cells therapy for arthritis can help any patient to recover from such a disease. By the way, without stem cells arthritis is a general term for joints inflammation, it brings together a group of joints inflammatory lesions of the various origins – infectious-allergic, traumatic, metabolic, degenerative, and reactive.
The most common reason to visit stem cell therapy for arthritis is the joints inflammation and as its result, an infection, or the infection source presence in the body. With the progression of the disease occurs complete destruction of the joint, resulting in impaired patient disability and worsening of life quality without treatment of arthritis with stem cell therapy in due time.
Adult autologous stem cells are the precursors of all the other cells in the body. Their unique feature is the ability to transform into other cells in tissues (i.e. differentiate). This property is used in stem cells therapy for many diseases, including arthritis, arthrosis, and osteochondrosis. For cell therapy of joint diseases the stem cells for arthritis treatment are taken from the patient’s bone marrow, fat or blood.
Next, after reaching a certain number of own stem cells they are administered to the patient’s affected joint. Such administration of stem cells does not require hospitalization and overrides ambulatory. Stem cells when injected into the cavity of the affected joint normalize metabolism, improving trophism and joint tissues, leading to a reduction of inflammation and recovery of joint mobility.
Moreover, stem cell therapy for arthrosis and other diseases enhances immunity to infections arising from common causes of joint damage. The special value of the use of stem cells is to stimulate cartilage regeneration and restoration of its structure. Treatment of diseases of the joints with mesenchymal stem cell therapy should start as early as possible until irreversible deformation of the joint has not happened yet.

Recent Comments